Perimeter Security
Round-the-clock monitoring no matter how challenging the conditions
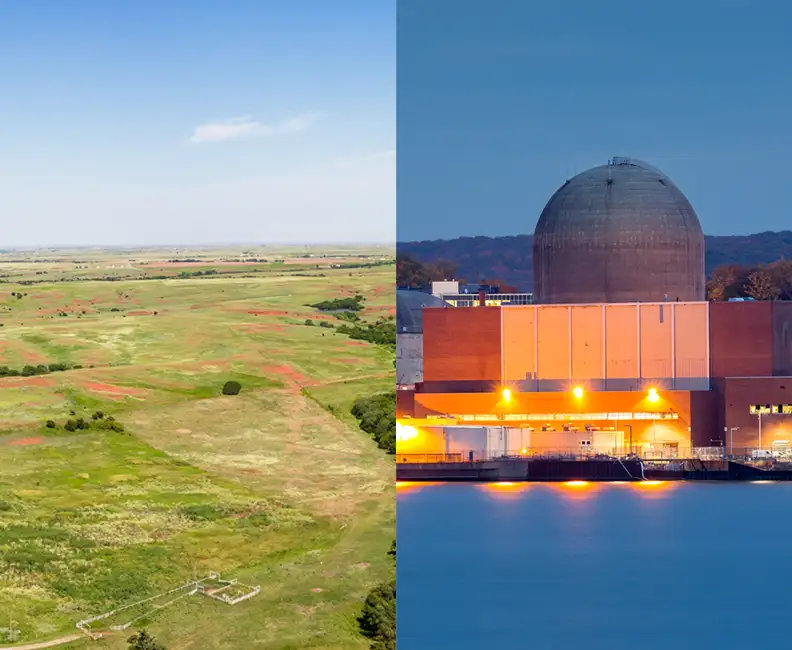
Safeguarding people, places and property is the aim of any kind of perimeter security – but that can be easier said than done in remote locations with difficult terrain or harsh weather conditions.
That’s why each solution is as individual as the site it is designed to protect – taking into account everything from timescales and budget to power and communications requirements.
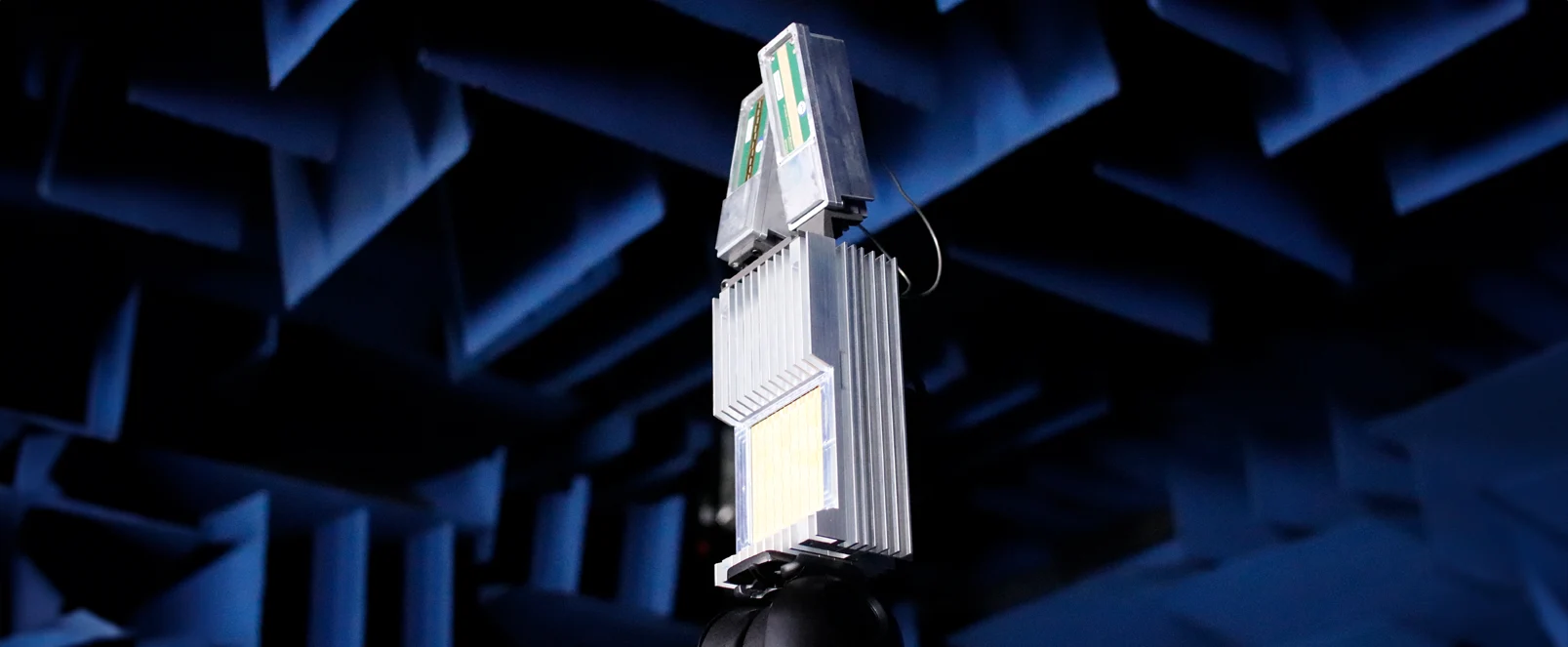
Compact and precise millimetre-wave (mmWave) radar is particularly suited to round-the-clock perimeter security solutions, either on its own or combined with infrared cameras, for example.
Ultra-fine range and Doppler resolution make it possible to see small moving objects even when much larger objects crowd the scene – and multiple units can be netted together to provide comprehensive coverage of even the most complex sites.
Real-world challenges
Key skills
-
Expertise with ultra-low size, weight, power and cost (SWaP-C) radars
Designing and fielding many different radar and communications systems to fit very tight operational constraints.
-
Nuanced understanding of imaging radars
Designing, building and fielding a number of radars that generate very fine range-velocity-angle images using established, as well as cutting-edge, techniques.
-
Configurable design approach
Easily able to design customised radar modules for a range of customer needs.
What sets us apart when it comes to perimeter security?
The Plextek team has extensive experience of using mmWave radar for perimeter security solutions. Our expertise in this field includes:
- Small covert sensors
- Sensitive site monitoring
- Hidden sensors for security
- Object classification with radars
- Drone surveillance
- Electronic security
- Imaging radars
- Intrusion detection with radars
- Long-range detection
- Motion sensors
- Perimeter protection
- Radar and communications systems design
- Radar detection theory
- Remote site monitoring
- Security integration
- Surveillance technologies