Alternative Navigation
Tailoring radar systems to the unique requirements of different applications
Alternative navigation offers a valuable lifeline in environments where traditional global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) are ineffective or unavailable.
Using tools and techniques ranging from simple inertial sensors found in smartphones to cutting-edge quantum gravity mapping, alternative navigation keeps everything on track underground, underwater, indoors and in urban canyons, and even in space.
Inertial navigation, visual scene matching, and acoustic or electromagnetic localisation are all examples of alternative navigation methods which allow systems to understand their location when GNSS is not available or is degraded.
The Plextek advantage

- Signal processing
Processing sensor data, such as accelerometers and gyroscopes, to estimate motion of a platform.
- Radio Frequency (RF) geolocation
Advanced RF geolocation techniques for detecting and locating objects, relying on years of experience in hardware development, antenna design and embedded signal processing.
- Electronics design
Delivering the intelligence that makes products work.
- Low size, weight, power and cost (SWAP-C)
Taking devices and optimising for embedded applications or designing custom hardware solutions for applications.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
Specialising in their application to RF, embedded hardware design and signal processing.
Alternative navigation capabilities
Navigating in areas where GNSS is degraded or unavailable usually requires expensive, specialised equipment. The challenge for the Plextek team was to create an accurate and low-cost alternative navigation system to enable a person to navigate accurately in the absence of GNSS.
The result was a system that attaches to a user’s boot and provides a highly accurate and robust position estimate when GNSS is ineffective or unavailable – inside buildings or tunnels, for example, or in an active GPS-denied environment.
The underpinning hardware and navigational algorithms offer low-drift alternative navigation capabilities in the event of GNSS signal loss. Read more: Alternative PNT
Developing an alternative navigation sensor
Autonomous Drones are increasing being used for a wide variety of applications but are generally heavily reliant on GNSS for navigation. Our challenge was to develop an alternative navigation sensor suitable for drones that could provide a GNSS-free navigation capability in all-weather day and night, and suitably small and low power.
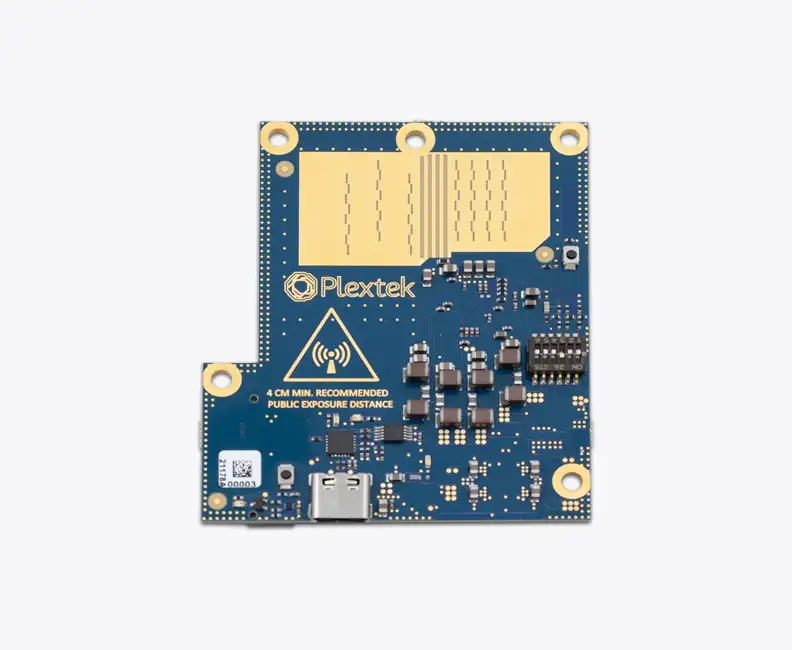
In response Plextek developed a proof-of-concept terrain referenced navigation (TRN) system using our miniature PLX-T60 radar. It compares the elevation profile of the ground beneath the drone to a digital elevation map to estimate the Drone’s location when GNSS is degraded or unavailable.
Use of radar is advantageous as, unlike camera technology, it can work equally well day and night and is not affected by inclement weather such as rain or fog. Read more on Augmenting UAV Safety with Ubiquitous Radar Technology.
ML techniques with Semantic segmentation

The challenge from the client was to take image retrieval to the next level – improving the performance of traditional visual scene matching (VSM) algorithms at finding the best matching image in a dataset of georeferenced images.
The Plextek team decided to augment the traditional VSM algorithms with one of the latest ML techniques – Semantic segmentation. This was used to assign a label to each pixel in an image, based on which category it belonged to – tree, person, vehicle, etc. This enabled the VSM algorithm to prioritise those features which are likely to remain consistent over time (such as buildings) over those that are likely to change (e.g. cars, vegetation). The result is a VSM algorithm that can more accurately estimate a system’s location by comparing imagery from a camera with a database of previously captured images. Read more on Semantic Segmentation in Visual Scene Matching.
What sets us apart when it comes to alternative navigation?
The Plextek team has a track record of delivering complex technology solutions covering a broad range of alternative navigation applications, including:
- Indoor
- Urban canyons
- Underground/underwater
- Military operations (GNSS denied)
- Space
Examples of our alternative navigation methods include:
- Computer vision
- Visual scene matching
- Radar terrain profile matching
- Simultaneous localisation and mapping (SLAM)
- Dead reckoning (inertial sensors)
- Acoustic localisation
- Electromagnetic localisation