The Challenge
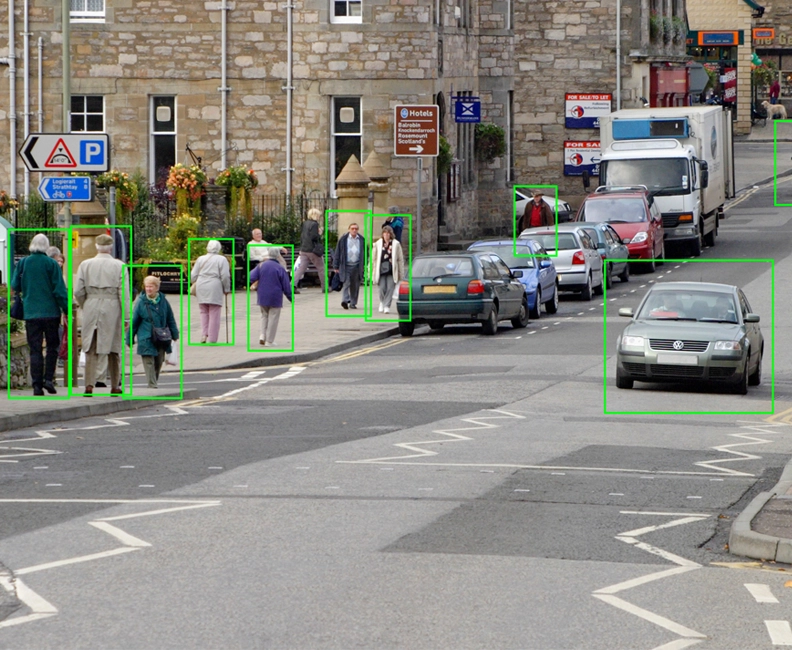
Visual Scene Matching (VSM) is the process of matching a newly captured image with a database of geotagged reference images to find the best match. This technique enables the construction of a track over time using the information from the best matches, which can be utilised as an Alternative Navigation System. Traditional algorithms that rely on features may face challenges when the scene has changed over time, such as seasonal variations like changes in vegetation or snow, as well as the presence of temporary elements like cars and pedestrians. These temporary features can significantly impact the performance of traditional algorithms.
The Approach
To address these challenges, a Semantic Segmentation algorithm was employed to predict the class of every pixel in the image, allowing the identification of temporary or changing features in the scene. This information was then used to guide feature extraction in specific regions of the scene. The features were extracted using Scale-Invariant Feature Transform (SIFT) within these regions and fed into a Vocabulary Tree algorithm for Visual Scene Matching. Various experiments were conducted to optimise the handling of temporary and changing features, such as removing features from these regions or applying blurring before feature extraction to reduce the extracted features. Additionally, experiments involved assigning different weights to features based on the class they were extracted from, such as assigning higher weights to features from signs and lower weights to features from trees.
The Outcome
By incorporating Semantic Segmentation to enhance the performance of the Vocabulary Tree algorithm, there was a notable 5.4%-point increase in image retrieval accuracy (from 78.4% to 83.3%), while still maintaining the interpretability of the traditional algorithm. This success has paved the way for a subsequent phase involving data fusion utilising a Particle Filter to generate trajectories using a larger dataset.
“Integrating Semantic Segmentation technology into the existing Visual Scene Matching process significantly improved the accuracy of image retrieval results. This advancement is crucial for industries where precise navigation and tracking are essential, such as autonomous vehicles, surveillance systems, and geographic information systems (GIS).”
Josip Rozman, Senior Consultant
The ability to adapt to changing environments and handle temporary scene variations is a key advantage of this approach, offering solutions for real-world applications requiring reliable and robust image matching capabilities.